What is Pile Foundation?
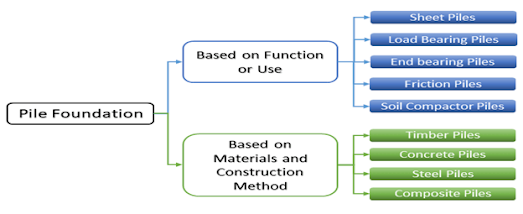
What is Pile Foundation? Foundations provide support to the structure, transfers the loads from the structure to the soil. But the layer at which the foundation transfers the load shall have an adequate bearing capacity and suitable settlement characteristics. When to Use Pile Foundation Following are the situations when using a pile foundation system can be } When the groundwater table is high. } Heavy and un-uniform loads from superstructure are imposed. } Other types of foundations are costlier or not feasible. } When the soil at shallow depth is compressible. } When there is the possibility of scouring, due to its location near the river bed or seashore, etc. } When there is a canal or deep drainage systems near the structure. } When soil excavation is not possible up to the desired depth due to poor soil condition. } When it becomes impossible to keep t...
