What is Pile Foundation?
What is Pile Foundation?
Foundations provide support to the structure, transfers the loads from the structure to the soil. But the layer at which the foundation transfers the load shall have an adequate bearing capacity and suitable settlement characteristics.
When to Use Pile Foundation
Following are the situations when using a pile foundation system can be
} When the groundwater table is high.
} Heavy and un-uniform loads from superstructure are imposed.
} Other types of foundations are costlier or not feasible.
} When the soil at shallow depth is compressible.
} When there is the possibility of scouring, due to its location near the river bed or seashore, etc.
} When there is a canal or deep drainage systems near the structure.
} When soil excavation is not possible up to the desired depth due to poor soil condition.
} When it becomes impossible to keep the foundation trenches dry by pumping or by any other measure due to heavy inflow of seepage.
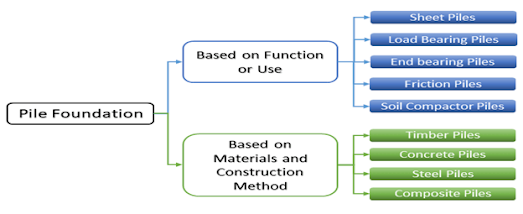
Types of Pile Foundation:-
Based on Function or Use:-
This type of pile is mostly used to provide lateral support. Usually, they resist lateral pressure from loose soil, the flow of water, etc. They are usually used for cofferdams, trench sheeting, shore protection, etc. They are not used for providing vertical support to the structure.
Load Bearing Piles:-
This type of pile foundation is mainly used to transfer the vertical loads from the structure to the soil. These foundations transmit loads through the soil with poor supporting property onto a layer which is capable of bearing the load. Depending on the mechanism of load transfer from pile to the soil, load-bearing piles can be further classified as flowed.
End Bearing Piles:-
In this type of pile, the loads pass through the lower tip of the pile. The bottom end of the pile rests on a strong layer of soil or rock. Usually, the pile rests at a transition layer of a weak and strong slayer. As a result, the pile acts as a column and safely transfers the load to the strong layer.
Friction Pile:-
Friction pile transfers the load from the structure to the soil by the frictional force between the surface of the pile and the soil surrounding the pile such as stiff clay, sandy soil , etc. Friction can be developed for the entire length of the pile or a definite length of the pile, depending on the strata of the soil. In friction pile, generally, the entire surface of the pile works to transfer the loads from the structure to the soil.
Soil Compactor Piles:-
Sometimes piles are driven at placed closed intervals to increase the bearing capacity of soil by compacting.
Based on Materials and Construction Method:-
Timber Piles:-
} Timber piles are placed under the water level. They last for approximately about 30 years. They can be rectangular or circular in shape. Their diameter or size can vary from 12 to 16 inches. The length of the pile is usually 20 times of the top width.
} They are usually designed for 15 to 20 tons. Additional strength can be obtained by bolting fish plates to the side of the piles.
Concrete Piles:-
Concrete Piles and drilled shafts are an important category of foundations. Despite their relatively high cost, they become necessary when we want to transfer the loads of a a heavy superstructure (bridge, high rise building, etc.) to the lower layers of soil. Another reason for choosing a pile foundation is the condition and quality of soil layers.
} Pre-cast Concrete Pile
} Cast-in-Palace Concrete Piles
Steel Piles:-
Steel piles may be of I-section or hollow pipe. They are filled with concrete. The size may vary from 10 inches to 24 inches in diameter and thickness is usually ¾ inches. Because of the small sectional area, the piles are easy to drive. They are mostly used as end-bearing piles.
Composite Piles:-
} Composite Piles are those piles of two different materials are driven one over the other, so as to enable them to act together to perform the function of a single pile. In such a combination, advantage is taken of the good qualities of both the materials. These prove economical as they permit the utilization of the great corrosion resistance property of one material with the cheapness or strength of the other.











Comments
Post a Comment